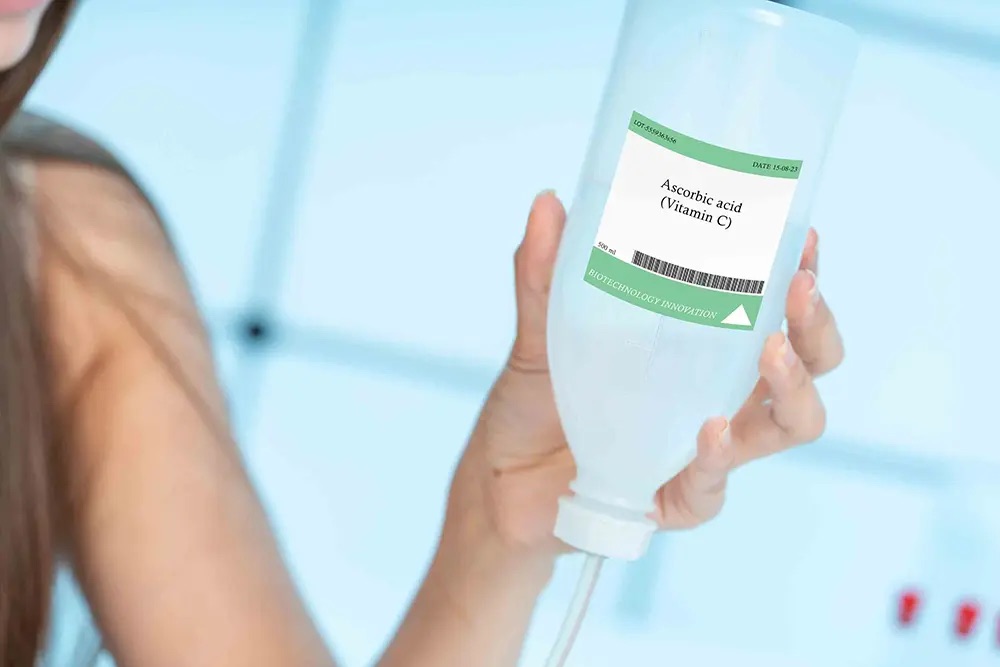
Intravenous Vitamin C
At Solea Medical Spa & Beauty Lounge, we administer intravenous injections of vitamin C. This is an innovative way to maintain beauty and skin health, as well as strong immunity. High doses of ascorbic acid are effective in treating skin inflammation, acne, wrinkles, rosacea, and couperose.
Vitamin therapy helps combat physical and psychological stress and reduces allergy symptoms. It also has a positive effect on the health of the heart, blood vessels, and respiratory system.
Treat now, Pay later
Ensuring Comfort During the Procedure
Experience the transformation you deserve. Our expert team tailors every treatment to your unique beauty goals, using cutting-edge technology in a luxurious, calming environment. Whether it’s laser therapy, facials, or body contouring – your journey to confidence starts here..
What is Intravenous Vitamin Therapy?
Vitamin therapy is a procedure of intravenous drip administration of a solution with vitamin C. It goes directly into the bloodstream, bypassing the stomach and intestines. Compared to oral administration, intravenous injections ensure the delivery of higher doses of vitamin C to the body.
Ascorbic acid or sodium ascorbate is dissolved in an infusion solution: 0.9% sodium chloride solution, 5% glucose solutions, or distilled water. The dosage of the drug and the volume of the solution are selected by a specialist on an individual basis.
Cases where intravenous therapy is administered include:
- Acute vitamin C deficiency.
- Conditions and diseases that require increased doses of ascorbic acid.
- Contraindications to orally taking supplements due to gastrointestinal tract diseases.
- Vitamin C is not absorbed through the intestine.
Vitamin C: Health Benefits
1Immune System Support
Vitamin C stimulates the production of leukocytes. White blood cells destroy and remove foreign proteins and toxins from the body and produce antibodies. Vitamin C also enhances the function of immune cells, increasing resistance to infections and other diseases.
2Antioxidant Protection
Vitamin C neutralizes free radicals, which trigger oxidative processes and damage healthy cells. This potentially reduces the risk of chronic diseases and cancer.
3Skin Regeneration
Ascorbic acid stimulates collagen production. This protein improves skin health and promotes wound healing. Consuming vitamin C supplements helps in the prevention and treatment of acne, rosacea, couperose, and in combating both large and fine wrinkles. Burns heal faster and more effectively.
4Cardiovascular Health
Vitamin C positively affects blood coagulability, helps lower blood pressure, and strengthens the walls of arteries and capillaries. Regular consumption of ascorbic acid lowers the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
5Respiratory System Strengthening
Vitamin C aids in treating bronchitis, pneumonia, and reduces the duration and severity of respiratory infections and asthma attacks.
6Eye Protection
Regular intake of vitamin C reduces the risk of age-related eye diseases and vision loss. It helps prevent the development of cataracts and retinal diseases.
7Stress Reduction
Due to its antioxidant properties, vitamin C reduces cortisol levels, a hormone produced due to stress. High cortisol levels can cause anxiety, sleep problems, negatively affect skin and muscle condition, lead to increased blood glucose levels and weight gain.
8Anemia Prevention
Vitamin C increases the efficiency of non-heme iron absorption, which is obtained from plant sources. Combined intake of these substances prevents iron-deficiency anemia in at-risk groups.
What Is Vitamin C IV Therapy Used For?
1Vitamin C Deficiency
A course of intravenous administration of high doses of vitamin C will be effective if you’re experiencing deficiency or scurvy. A lack of ascorbic acid manifests as increased fatigue, body aches, fragility of blood vessels, bruising, and bleeding gums.
Vitamin C deficiency often occurs in cases of:
– poor nutrition;
– limited intake of fruits and vegetables;
– active/passive smoking;
– gastrointestinal diseases (ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s – disease, intestinal malabsorption, and others);
– certain types of cancer.
2Serious Injuries
Vitamin C is crucial in the treatment of thermal burns, including severe ones. Vitamin C therapy enhances the quality of healing and decreases the amount of time it takes, hence aiding patients in recovering faster.
Ascorbic acid reduces oxidative stress and normalizes fibroblast function. These cells produce collagen, elastin, and hyaluronic acid, components necessary for normal skin recovery. Vitamin C improves microcirculation, reduces the fluid requirement in burn patients, strengthens immunity, and decreases the risk of infection by infectious agents.
3Infections
With adequate intake of vitamin C, the ability of leukocytes to absorb pathogenic microorganisms is enhanced. The level of neutrophils in the blood increases. These cells are responsible for the bactericidal indicators of the blood. Intravenous vitamin therapy reduces the risk of respiratory infections and eases their progression. It is prescribed for frequent colds and chronic pathologies of ENT organs.
4Cancer
The effect of ascorbic acid on cancer cells is still actively being studied. Some research confirms that large intravenous doses of vitamin C can damage cancer cells while leaving healthy cells unharmed. At high concentrations, ascorbic acid leads to the formation of free radicals. These radicals synthesize toxic hydrogen peroxide. Healthy cells produce an enzyme that breaks down hydrogen peroxide. Malignant cells lack this enzyme, so they decompose under the action of the peroxide.
5Atherosclerosis
Ascorbic acid affects the metabolism of fatty acids and blood cholesterol levels. Even after a single intravenous administration, its content decreases. Course treatment and continued consumption of sufficient vitamin C prevent the formation of new atherosclerotic plaques and reduce the risk of developing ischemic heart disease.
6Allergic Reactions
Vitamin C mitigates respiratory and skin symptoms of seasonal allergies. Intravenous administration has been noted to reduce rash, runny nose, tearing, and episodes of shortness of breath.
Contraindications to Vitamin C Therapy
- Hypervitaminosis of vitamin C. This is detected before therapy through a blood test.
- Individual intolerance to ascorbic acid supplements. Allergy diagnostics for vitamin C is carried out by a blood test to determine immunoglobulin E.
- Hemochromatosis. A hereditary disease in which the body absorbs and accumulates more iron than needed.
- Renal dysfunction. Including nephrolithiasis, or the presence of risk factors for urinary system pathologies.
Hemochromatosis. A hereditary disease in which the body absorbs and accumulates more iron than needed. - Deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD). A genetic defect where high doses of vitamin C cause the destruction of red blood cells.
Other IV Drips